The Magnet
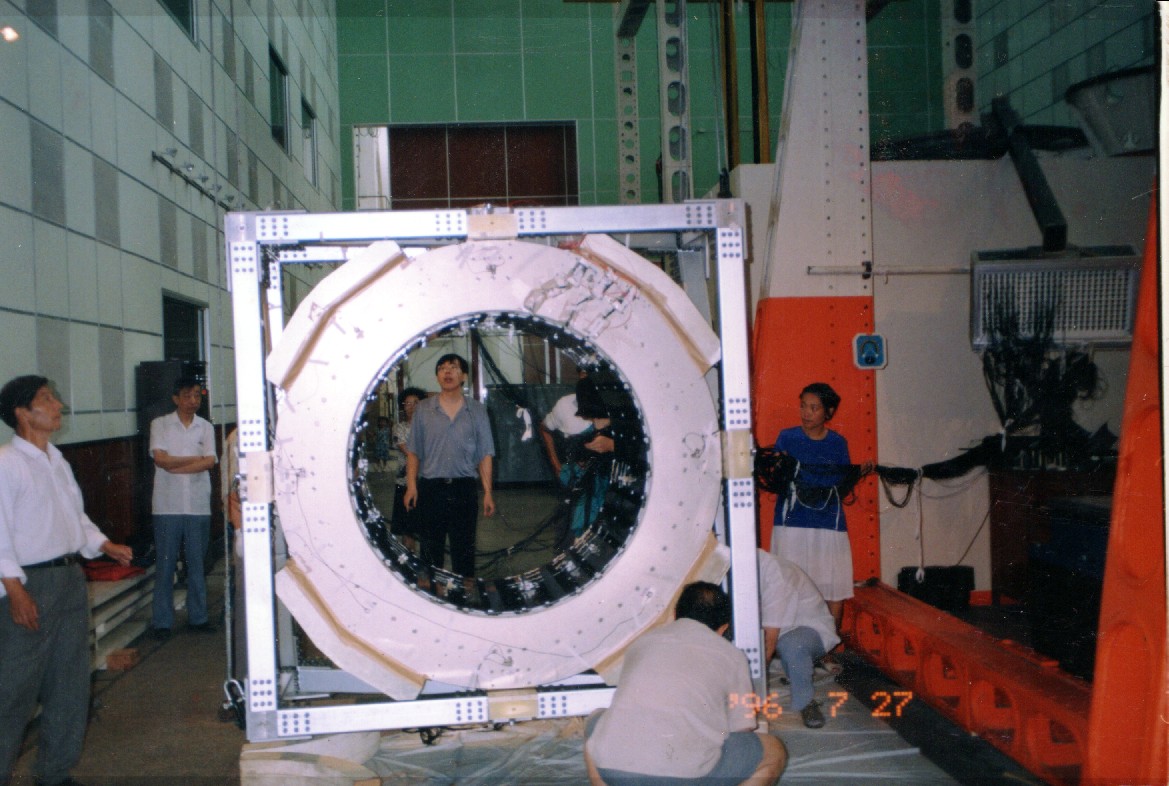
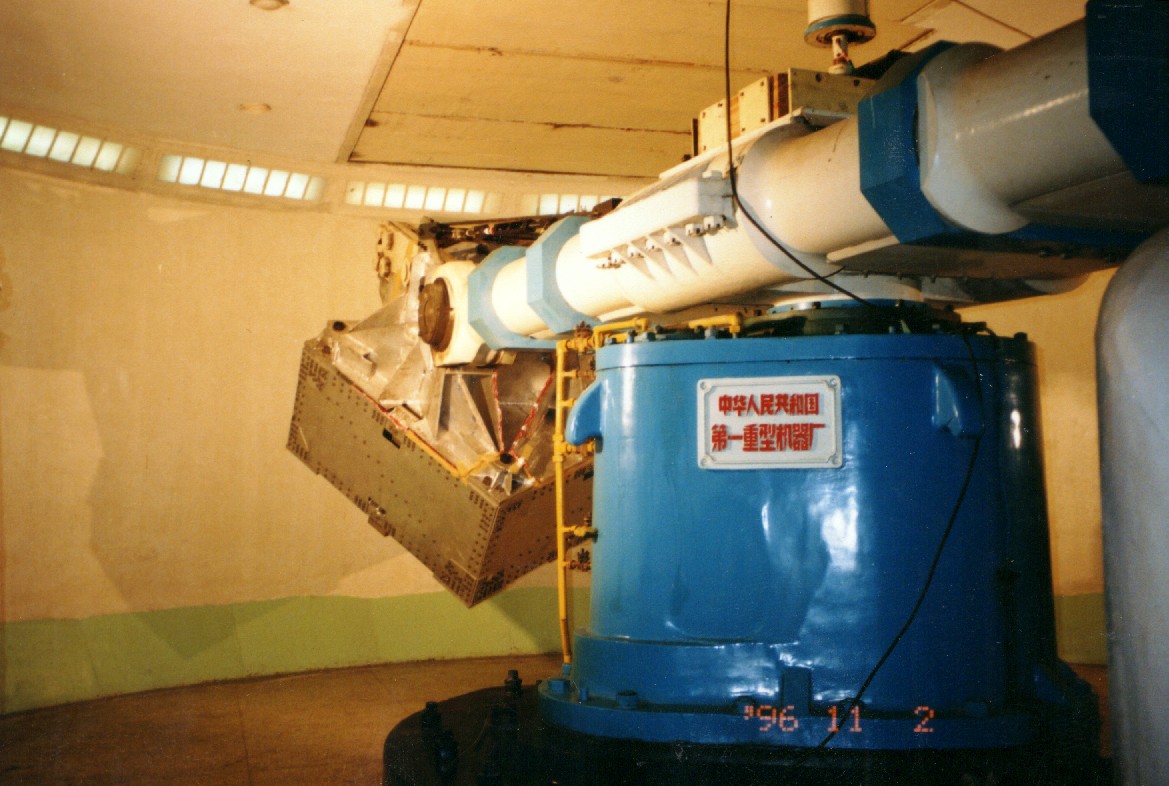
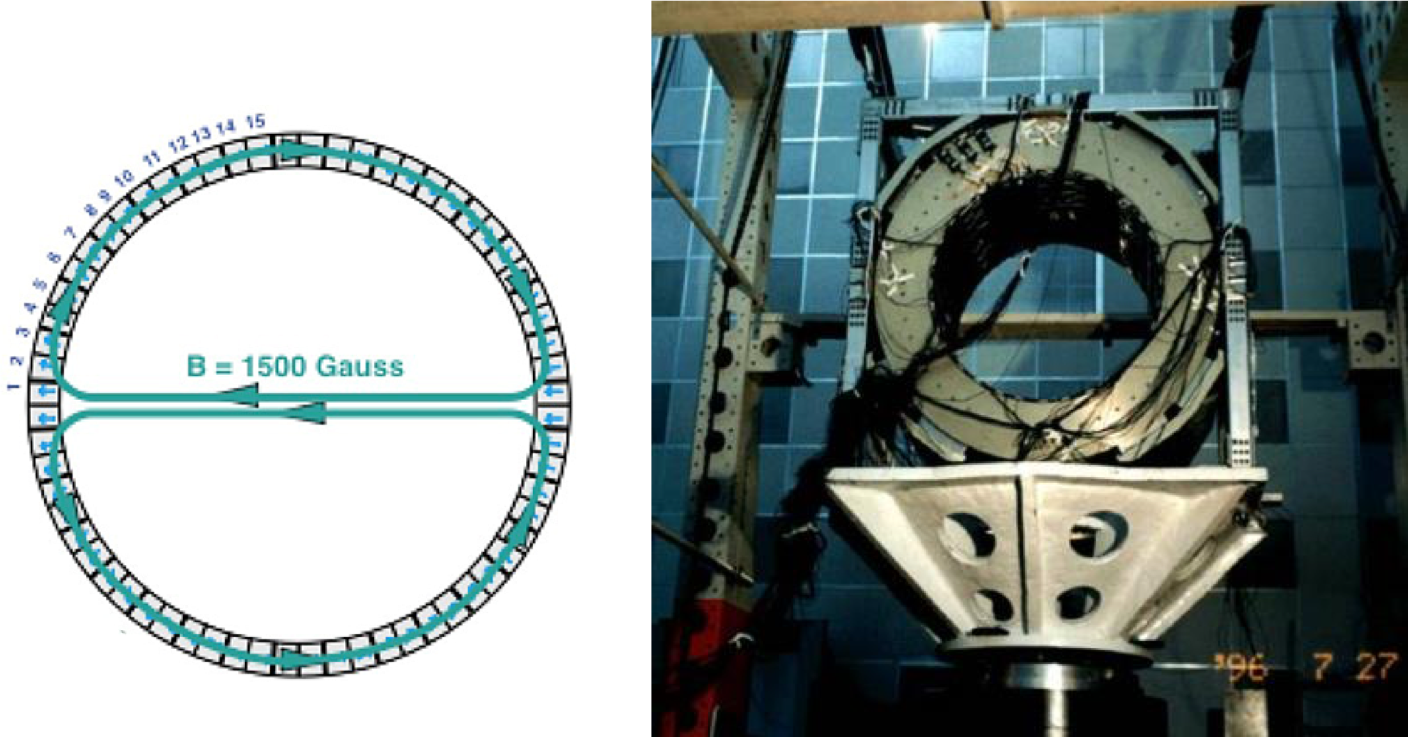
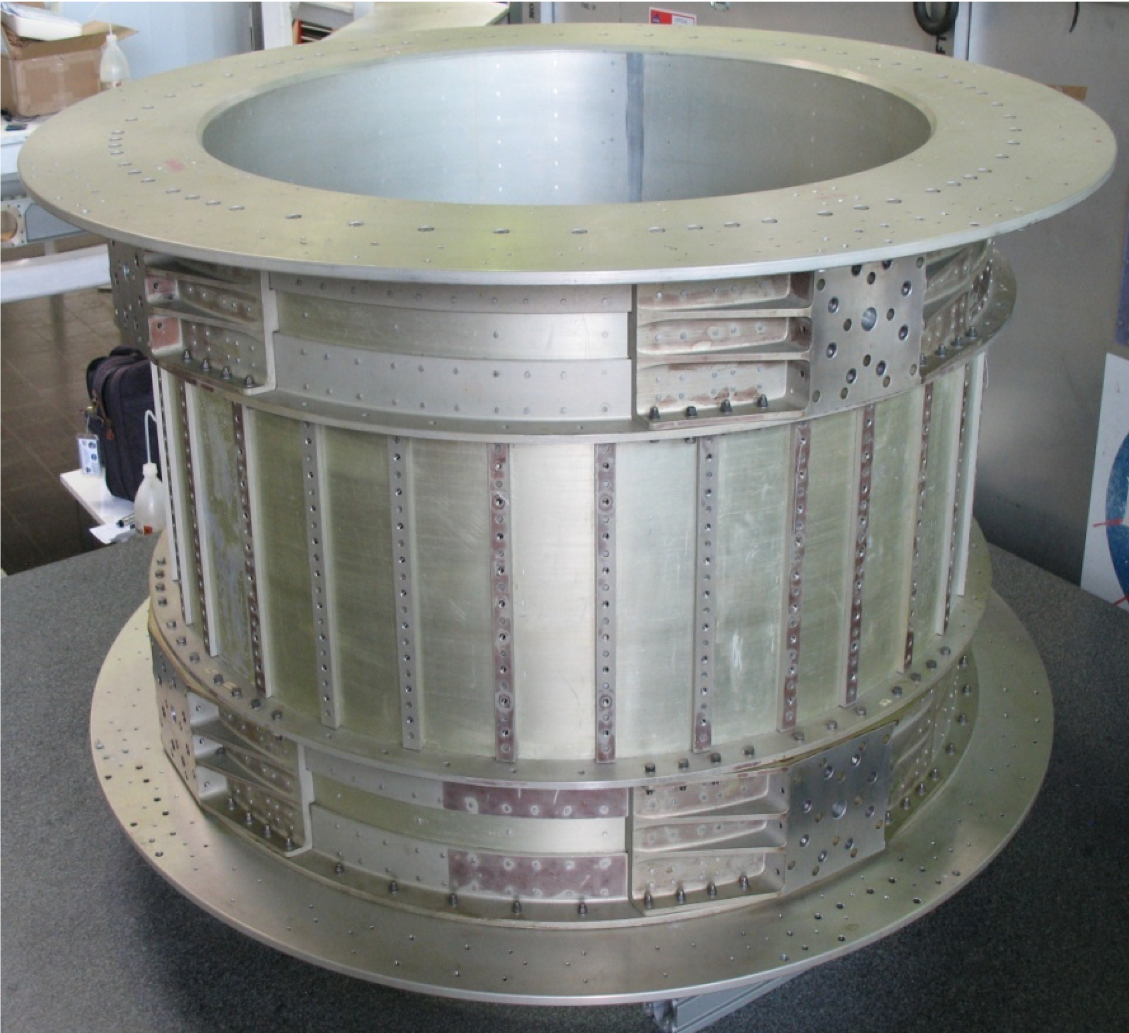
The magnet, shown in Figure 1 and 2, is made of 64 high-grade Nd-Fe-B sectors assembled in a cylindrical shell structure 0.8 m long with an inner diameter of 1.1 m. This configuration produces a field of 1.4 kG in the $x$ direction at the center of the magnet and negligible dipole moment outside the magnet. This is important in order to eliminate the effect of torque on the Space Station. Figure 3 shows the detailed three-dimensional field of the magnet mapped in 2010. The field was measured in 120 000 locations to an accuracy of better than 1%. Comparison with the measurements performed with the same magnet in 1997, before the engineering flight of AMS-01, shows that the field did not change within 1%, limited by the accuracy of the 1997 measurement. Together with the tracker, the magnet provides a maximum detectable rigidity of 2 TV on average, over tracker planes 1-9, where rigidity is the momentum divided by the charge. Figure 4 and Figure 5 show the vibration test and static load test carried out in 1996 in China.