![]() Cosmos is the ultimate laboratory, where cosmic rays can be observed at energies higher than any accelerator. Charged cosmic rays have mass, and they are absorbed by the 100 km of Earth’s atmosphere (10 m of water). To study the intrinsic properties of charged cosmic rays requires a detector above the Earth’s atmosphere.
Cosmos is the ultimate laboratory, where cosmic rays can be observed at energies higher than any accelerator. Charged cosmic rays have mass, and they are absorbed by the 100 km of Earth’s atmosphere (10 m of water). To study the intrinsic properties of charged cosmic rays requires a detector above the Earth’s atmosphere.
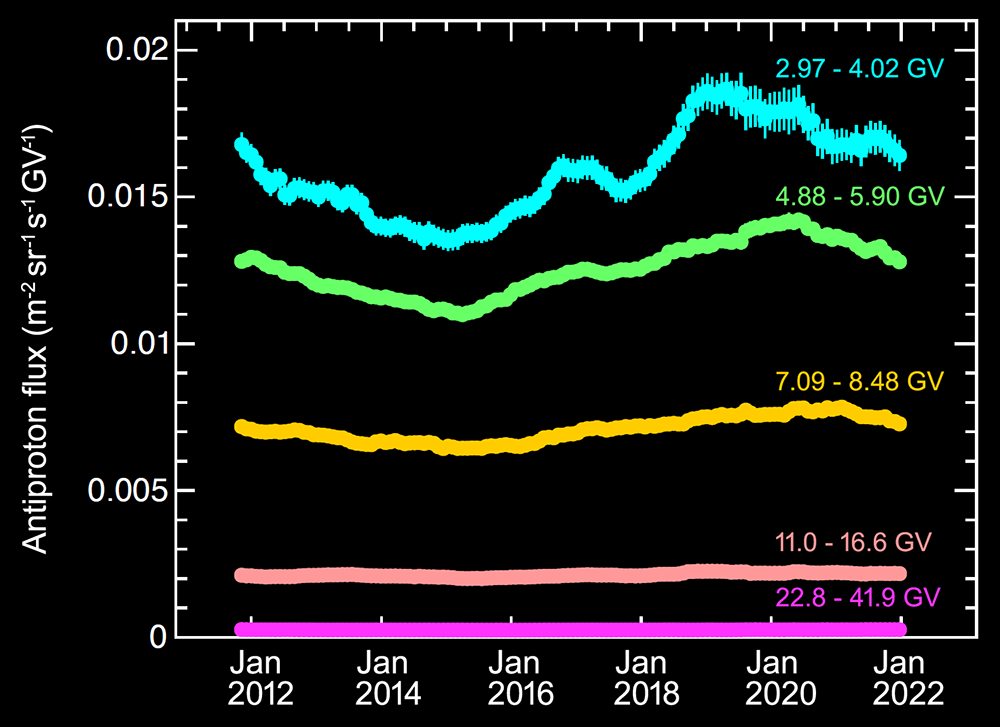
AMS, the magnetic spectrometer operating on the International Space Station (ISS), is the only way to provide long term (20 years) precision measurements of charged cosmic rays.
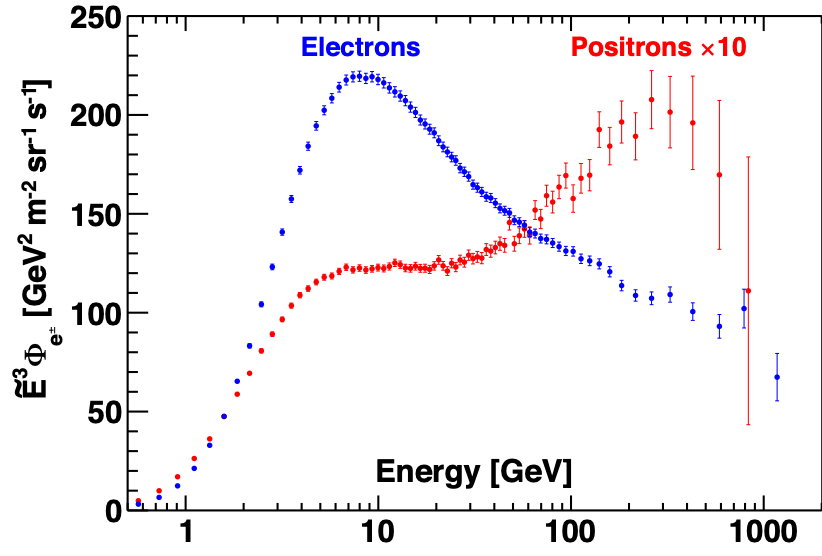
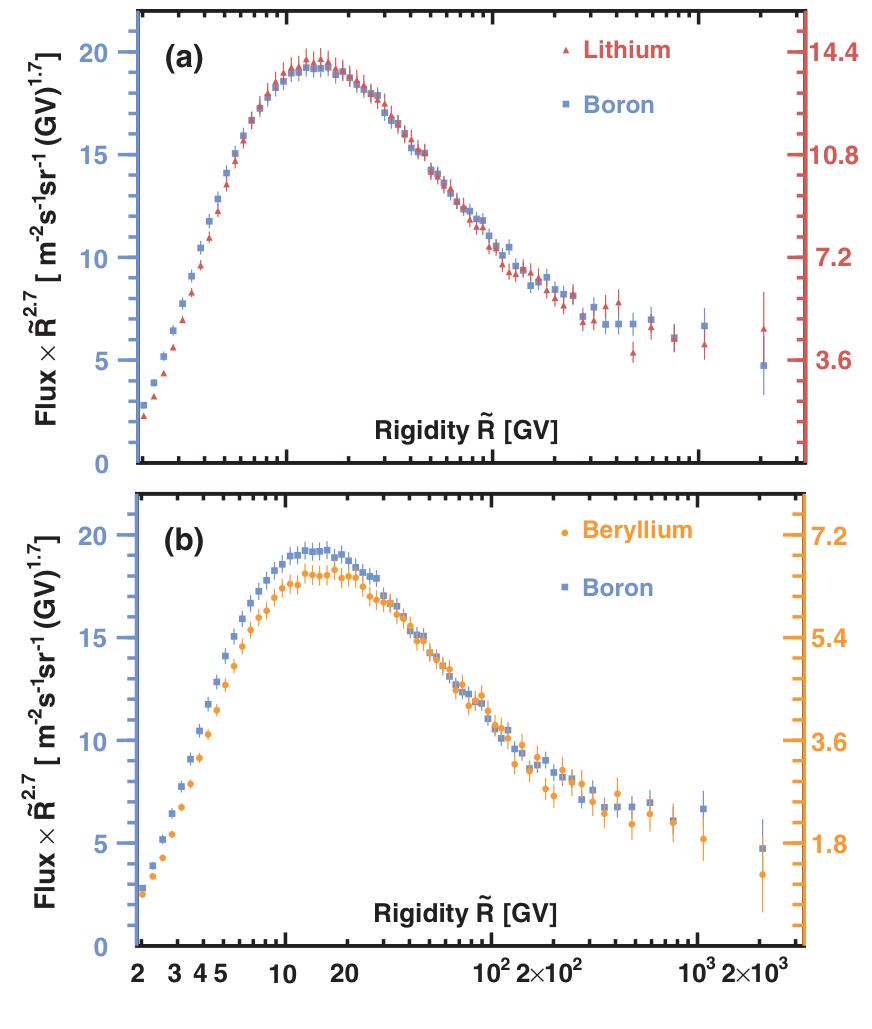
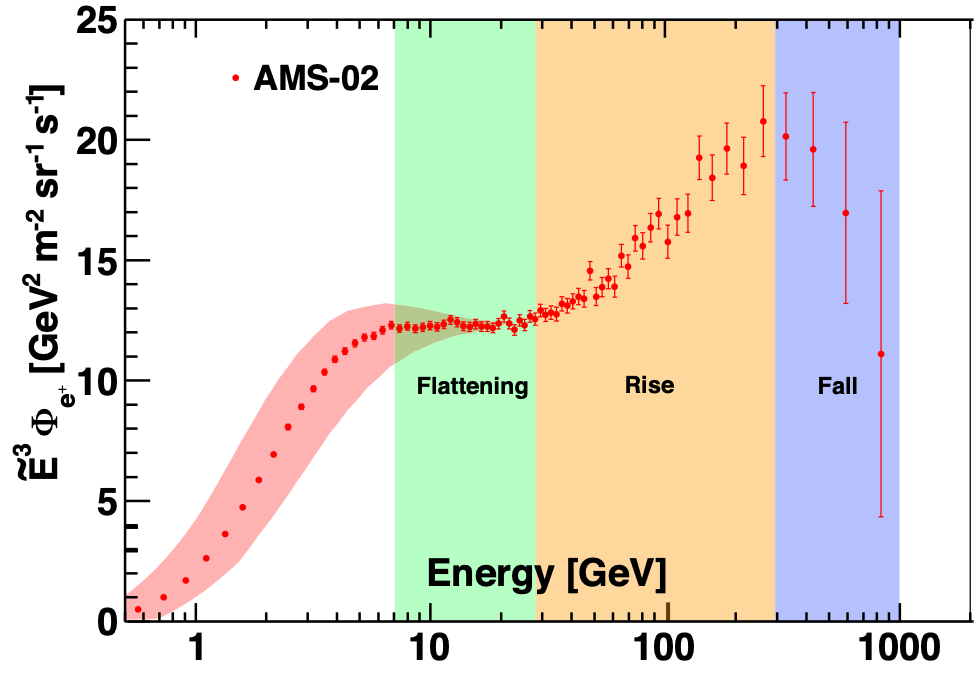
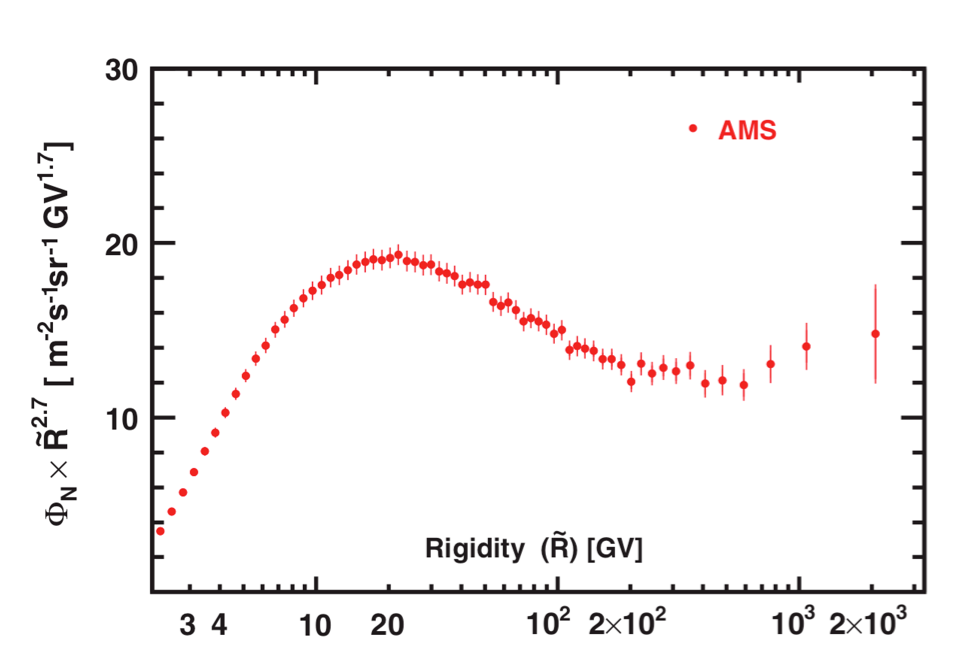
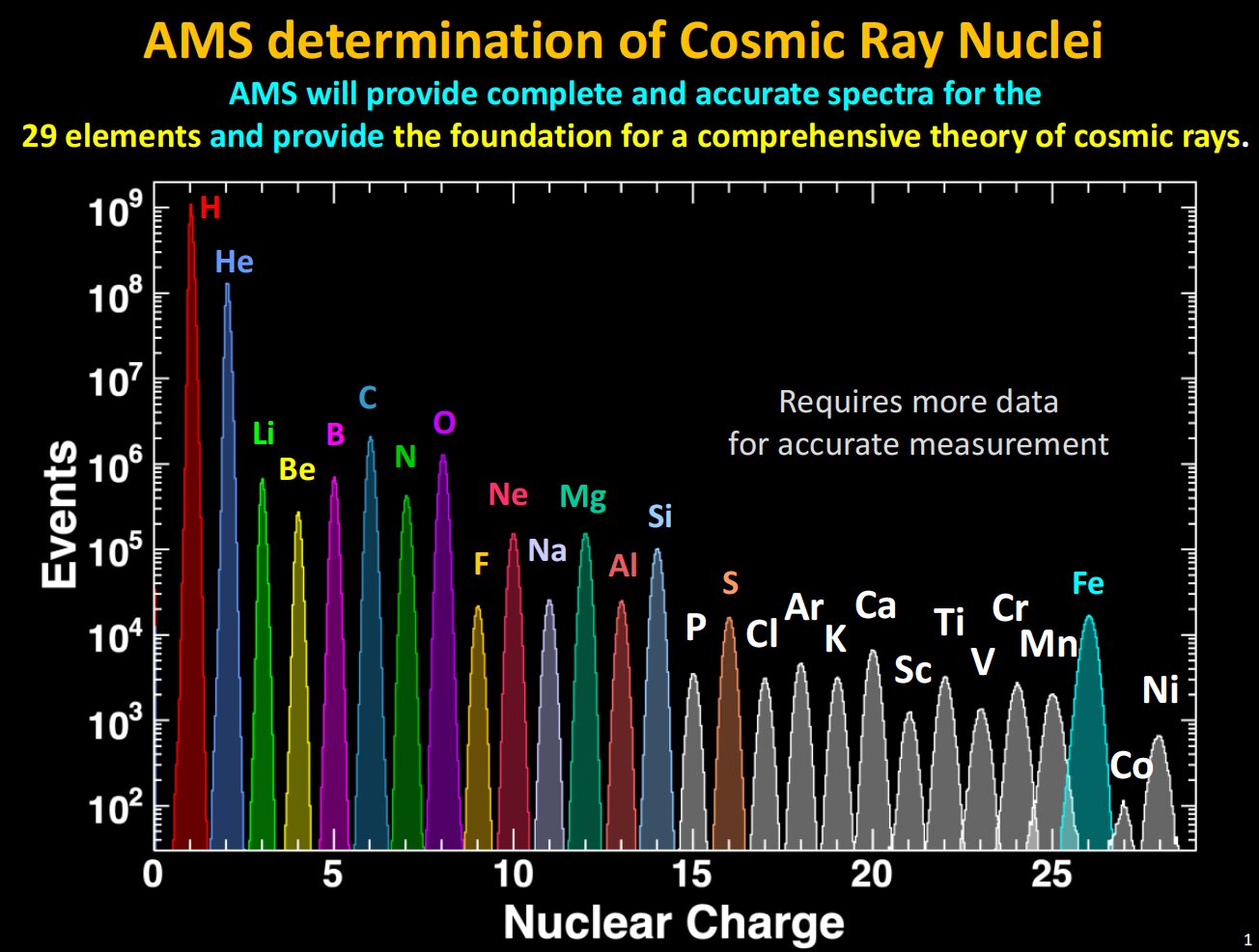
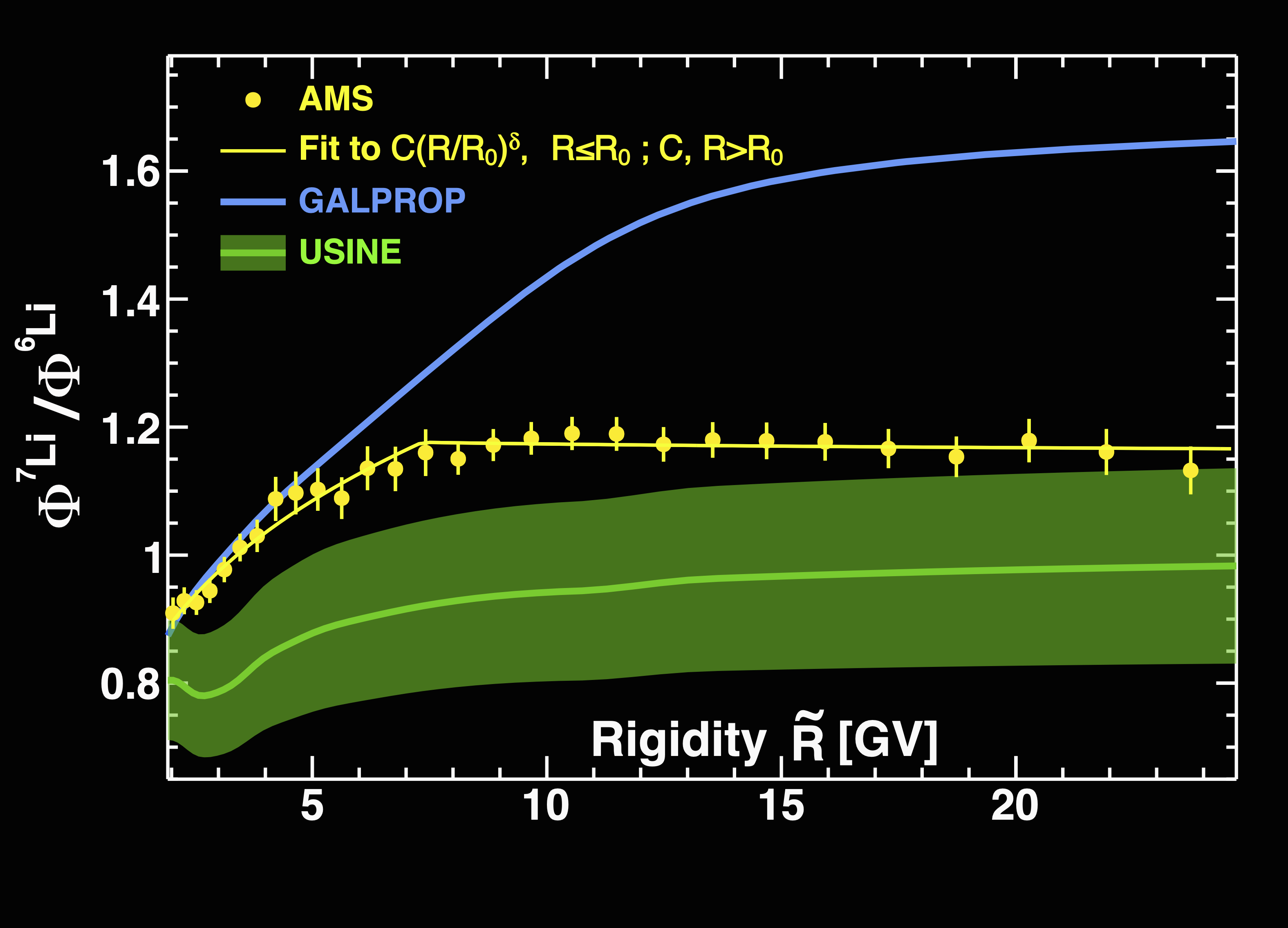
AMS uses the unique environment of space to advance the knowledge of the universe and to contribute to the understanding of its structure and origin by searching for the missing antimatter, by exploring the origin of dark matter and by measuring with the highest accuracy the composition of cosmic rays in the multi TeV region of energy.