25.041311, 121.616657
Academia Sinica Grid-computing Centre (ASGC)
Academia Sinica Grid-computing Centre (ASGC) was established in 2005 to join the World-wide Large Hadron Collider Computing Grid (WLCG) as one of the eleven Tier-1 centers and the only one in Asia. WLCG played a crucial role in the discovery of the Higgs particle in 2012. Currently about 300 computing centers of the major research institutions around the world are linked by WLCG. Based on the technologies and experiences of WLCG, ASGC has been developing the distributed cloud operating system (DiCOS) to support broader disciplines of research applications in Academia Sinica and international collaborations including physical science (such as experiments of ATLAS, AMS, Gravitational Waves (LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA), and TEXONO, advanced researches in novel materials and lattice gauge theory), bio-science, environmental and earth science, as well as machine learning and data sciences. ASGC is facilitating GPU, container, parallel computing and working on improving system efficiency for e-Science. By actively participating in the internationally collaborated WLCG project as a Tier-1 center, ASGC stays in the forefront of distributed computing technology. As one of the world’s leading research cloud centers, we are poised to support the advanced computing needs of AS researches based on cloud computing.
Our strategy is to grow the distributed cloud computing technologies and applications progressively through collaborations with AS research projects as well as technologies developed from international collaborations such as WLCG and EGI. One of recent successful cases is the support of AS Cryo-EM (Electron Microscope) and synchrotron-based protein structure researches. ASGC customized the workflow by integrating big data storage, process, analysis, web portals, and authentication and authorization infrastructure for AS Cryo-EM community according to their computing models. Apart from further improvement of GPU and container computing technologies, ASGC also minimized the data movement cost and developed flexible user environment and interfaces of DiCOS by Jupyter hub/notebook. ASGC aims to achieve O(1000)PB scale data processing capability of DiCOS in next 5 years.
Contribution to AMS
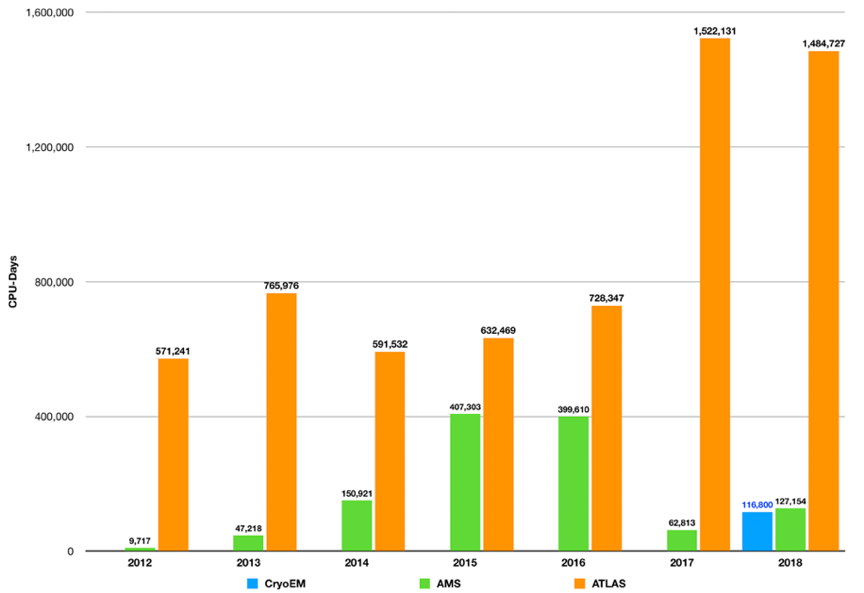
The first MPI cloud computing services at ASGC were developed based on the requirements of AMS. ASGC supports the AMS data reproduction required from time to time due to the upgrade of the reconstruction software as well as the huge simulation events needed to search for anti-deuterium, anti-helium, anti-carbon and anti-oxygen for understanding the origin of antimatter in the Universe. AMS jobs are running by dynamically created virtual machines over the allocated 3,000 CPU cores through DiCOS. More than 1.2M CPU-days computing resources have been used by AMS jobs from 2012. ASGC also provides high-performance data transmission for AMS between CERN and Taiwan through ASGCNet. AMS is the second largest user communities at ASGC in terms of CPU usage as depicted in Figure 1.